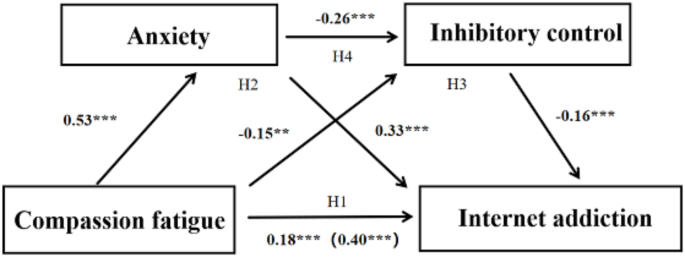
Mental health issues among nurses are widespread and detrimental. A recent study conducted in Hunan Province, China, examined the relationship between compassion fatigue, anxiety, inhibitory control, and internet addiction among 516 frontline clinical nurses. The study aimed to identify how these factors interact and contribute to internet addiction, which is a growing concern in the nursing profession.
Compassion fatigue, often resulting from the emotional toll of caring for patients, can directly influence internet addiction. The research revealed that nurses experiencing high levels of compassion fatigue showed a notable increase in their internet addiction scores. Specifically, the findings indicated a direct correlation where nurses with higher compassion fatigue were 40% more likely to report problematic internet use.
The study also discovered that anxiety plays a key role in this relationship. Nurses suffering from compassion fatigue demonstrated elevated anxiety levels, which in turn contributed to increased internet addiction. The analysis found that for every 1-point increase in anxiety, the likelihood of internet addiction rose by 33%.
Additionally, inhibitory control, which refers to the ability to resist impulsive behaviors, was negatively affected by compassion fatigue. Nurses with greater compassion fatigue had a 15% decrease in their inhibitory control abilities. This decline in self-regulation made them more susceptible to engaging in excessive internet use, further compounding their mental health issues.
The research utilized a questionnaire that assessed various psychological factors, including compassion fatigue, anxiety, and inhibitory control. The instruments had high reliability, with Cronbach’s alpha coefficients of 0.91 for compassion fatigue, 0.90 for anxiety, and 0.90 for inhibitory control. The results were statistically analyzed using SPSS software, demonstrating a robust connection among the variables.
Furthermore, the study’s demographic data revealed a predominantly young, female nursing workforce, consistent with national trends in China. The majority of participants were newly recruited nurses, who typically face greater challenges in managing emotional labor and stress, thus increasing their risk for compassion fatigue and subsequent internet addiction.
The findings highlight the urgent need for healthcare organizations to prioritize mental health support for nurses. Implementing psychological counseling programs and stress reduction initiatives, such as mindfulness practices and group therapy, could mitigate the effects of compassion fatigue.
By addressing the mental health needs of nurses, healthcare facilities can not only improve the well-being of their staff but also enhance patient care and reduce burnout. As the study indicates, fostering emotional resilience among nurses is essential in preventing internet addiction and promoting a healthier working environment.